Crypto Bridges Explanation & How to Use Safely 2026
Learn what a crypto bridge is, how it works, and how to use crypto bridges safely while transferring assets across blockchains.
As blockchain ecosystems continue to expand, users are no longer limited to a single network. From Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain to Solana, Polygon, and Layer-2 solutions, each blockchain offers unique advantages. However, these networks do not naturally communicate with one another. This limitation gave rise to a critical piece of infrastructure known as the crypto bridge. Understanding what a crypto bridge is and how to use it safely has become essential for anyone navigating today’s multi-chain crypto landscape.
A crypto bridge enables users to transfer digital assets, data, or messages between different blockchains. Without bridges, liquidity would remain fragmented, decentralized applications would be isolated, and users would face significant barriers when moving funds. Yet, despite their usefulness, crypto bridges are also among the most targeted components in the blockchain ecosystem due to security vulnerabilities and complexity.
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of what a crypto bridge is, how it works, the different types of bridges, and most importantly, how to use a crypto bridge safely. Whether you are a beginner exploring decentralized finance or an experienced trader interacting across multiple chains, this guide will help you make informed decisions while minimizing risk.
What a Crypto Bridge Is
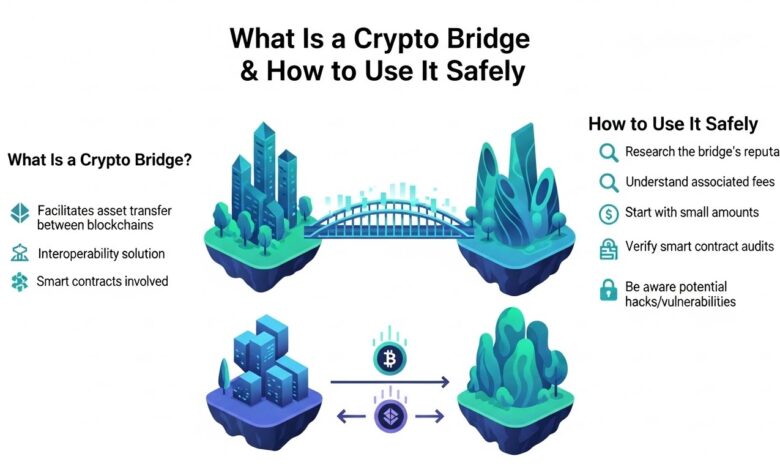
A crypto bridge is a protocol that connects two or more blockchains, allowing assets and information to move between otherwise incompatible networks. Since most blockchains operate independently with their own consensus rules and architectures, they cannot directly recognize assets from other chains.
Crypto bridges solve this problem by creating a mechanism that locks, burns, or escrows assets on one blockchain while issuing an equivalent representation on another. This process allows users to maintain value while participating in different ecosystems. For example, bridging ETH from Ethereum to a Layer-2 network enables users to enjoy lower transaction fees without selling their assets.
In essence, crypto bridges serve as the backbone of blockchain interoperability, a concept that has become increasingly important as decentralized applications and multi-chain strategies grow in popularity.
How Crypto Bridges Work
Lock-and-Mint Mechanism
The most common way a crypto bridge functions is through a lock-and-mint model. When a user initiates a transfer, the original asset is locked in a smart contract on the source blockchain. Once confirmed, the bridge mints a wrapped or synthetic version of that asset on the destination chain.
This wrapped asset represents the original token at a 1:1 ratio and can be used within the new ecosystem. When the user wants to return the asset, the wrapped version is burned, and the original token is unlocked on the source chain.
This mechanism ensures that the total supply remains consistent across chains while enabling seamless asset movement.
Burn-and-Mint Model
Another approach used by some crypto bridges is the burn-and-mint model. Instead of locking assets, tokens are permanently destroyed on the source chain and newly minted on the destination chain.
This method is often used in native cross-chain architectures where tokens are designed to exist on multiple networks. While efficient, it requires strong trust in the bridge’s smart contracts and validators.
Role of Validators and Oracles
Many crypto bridges rely on validators, relayers, or oracles to verify transactions across blockchains. These entities confirm that assets have been locked or burned before triggering the corresponding action on the destination chain.
The security and decentralization of these validators play a crucial role in determining how safe a crypto bridge is. Centralized validators can process transactions faster but introduce higher counterparty risk.
Types of Crypto Bridges
Centralized Crypto Bridges
Centralized bridges are operated by a single entity or organization. They typically offer faster transactions, user-friendly interfaces, and customer support. However, users must trust the operator to manage funds securely.
While centralized bridges are often easier for beginners, they contradict the core principles of decentralization and can become single points of failure.
Decentralized Crypto Bridges
Decentralized bridges rely on smart contracts and distributed validator networks to process transfers. These bridges align more closely with the ethos of blockchain technology by reducing reliance on a single authority.
Although decentralized bridges offer greater transparency, they can be more complex to use and may suffer from smart contract vulnerabilities if not properly audited.
Trusted vs. Trustless Bridges
Trusted bridges require users to place faith in an intermediary or group of validators. Trustless bridges, on the other hand, use cryptographic proofs and automated smart contracts to minimize human involvement.
Understanding this distinction is key when evaluating crypto bridge security and deciding which solution best suits your risk tolerance.
Why Crypto Bridges Are Important
Crypto bridges play a vital role in unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology. By enabling interoperability, they allow users to access decentralized finance protocols, NFT marketplaces, and gaming ecosystems across different networks.
They also help reduce congestion on popular chains like Ethereum by allowing users to move assets to Layer-2 or alternative blockchains with lower fees. This flexibility improves user experience and encourages broader adoption of blockchain applications.
Without crypto bridges, the crypto ecosystem would remain fragmented, limiting innovation and liquidity.
Risks Associated With Crypto Bridges
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
One of the biggest risks in using a crypto bridge lies in smart contract exploits. Since bridges handle large volumes of assets, they are attractive targets for hackers. A single vulnerability can lead to significant losses.
Even audited contracts are not immune, making it essential for users to understand the inherent risks before bridging assets.
Centralization and Governance Risks
Bridges with centralized governance structures may be susceptible to mismanagement, censorship, or insider threats. If a small group controls validator operations, the system’s resilience is compromised.
Liquidity and Slippage Issues
Some crypto bridges rely on liquidity pools. If liquidity is insufficient, users may experience delays, failed transactions, or unfavorable exchange rates when bridging assets.
How to Use a Crypto Bridge Safely
Research the Bridge Thoroughly
Before using any crypto bridge, it is crucial to research its reputation, development team, and security history. Look for bridges that have undergone multiple independent audits and have a strong track record.
Community feedback and transparency are often good indicators of reliability.
Start With Small Test Transactions
When using a crypto bridge for the first time, always begin with a small amount. This approach allows you to understand the process and confirm that everything works as expected before transferring larger sums.
Verify Contract Addresses and URLs
Phishing attacks are common in the crypto space. Always double-check the bridge’s official website and smart contract addresses. Bookmark trusted URLs and avoid clicking on links from unknown sources.
Use Hardware Wallets and Security Tools
Using a hardware wallet adds an extra layer of protection when interacting with crypto bridges. Combined with secure browsers and wallet extensions, this significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Monitor Network Conditions
High congestion or network instability can increase transaction failure rates. Timing your bridge transactions during periods of lower activity can improve reliability and reduce fees.
Popular Use Cases for Crypto Bridges
Accessing DeFi Across Chains
Crypto bridges enable users to move assets into different DeFi ecosystems, allowing them to participate in lending, staking, and yield farming opportunities across multiple networks.
NFT and Gaming Interoperability
Bridges also support cross-chain NFT transfers, making it possible to trade or use digital assets across various marketplaces and games.
Reducing Transaction Costs
By bridging assets to lower-fee networks, users can save significantly on gas fees while maintaining exposure to their preferred tokens.
The Future of Crypto Bridges
As blockchain adoption grows, crypto bridges are expected to become more secure, efficient, and user-friendly. Innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs, cross-chain messaging, and modular blockchains aim to reduce risks and improve scalability.
Regulatory clarity may also influence bridge development, encouraging higher security standards and greater transparency. In the long term, seamless interoperability could become a standard feature rather than a specialized tool.
Conclusion
Understanding what a crypto bridge is and how to use it safely is essential in today’s interconnected blockchain environment. Crypto bridges empower users to move assets freely across networks, access diverse applications, and optimize costs. However, these benefits come with risks that require careful consideration.
By choosing reputable bridges, practicing strong security habits, and staying informed about emerging technologies, users can significantly reduce potential threats. As the crypto ecosystem evolves, crypto bridges will remain a cornerstone of blockchain interoperability and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is a crypto bridge in simple terms?
A crypto bridge is a tool that allows you to transfer digital assets from one blockchain to another while maintaining their value.
Q. Are crypto bridges safe to use?
Crypto bridges can be safe if used carefully, but they carry risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and centralization issues.
Q. What happens to my tokens when I use a crypto bridge?
Your tokens are either locked or burned on the source chain, and an equivalent version is issued on the destination chain.
Q. Why do hackers target crypto bridges?
Crypto bridges often hold large amounts of assets, making them attractive targets for exploitation and attacks.
Q. How can beginners reduce risks when using crypto bridges?
Beginners should start with small transactions, use reputable bridges, verify addresses, and secure their wallets with strong security measures.